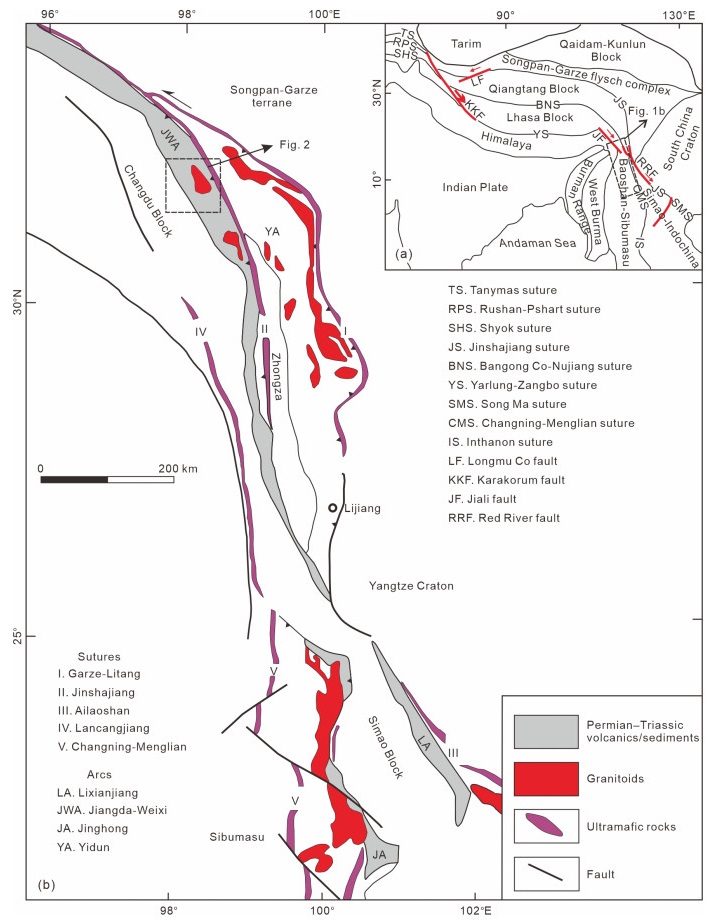
Permian–Triassic granitoids are widely distributed along the Jinshajiang suture belt, eastern Tibet, and are regarded as the result of the tectonic-magmatic activity associated with the evolution of Paleo-Tethys Ocean. This paper focuses on the high-K calc-alkaline I-type Rennong (~235 Ma) and Jiaduoling (~232 Ma) granitoid plutons, eastern Tibet, which are enriched in light rare earth elements (LREEs) and large ion lithophile elements (LILEs), but depleted in high field strength elements (HFSEs) with moderate-weak negative Eu anomalies (0.61–0.90). The Rennong granites are characterized by uniform zircon
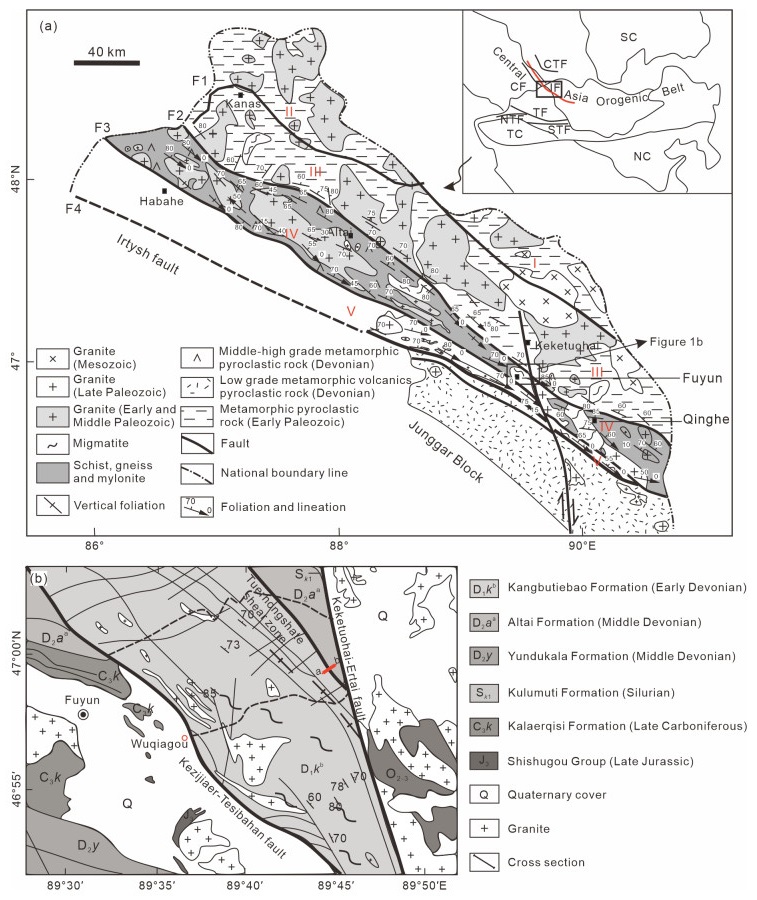
The Irtysh tectonic belt lies on the southern margin of the Chinese Altai Orogen. Several secondary shear zones with NW-SE strikes have developed in this tectonic belt, and the deformation processes are of great significance to understanding the tectonic regime of the Altai Orogen in the Late Paleozoic. The Tuerhongshate ductile shear zone is located in the eastern Irtysh tectonic belt with obvious deformed structures. The felsic rocks are strongly mylonitized, exhibiting
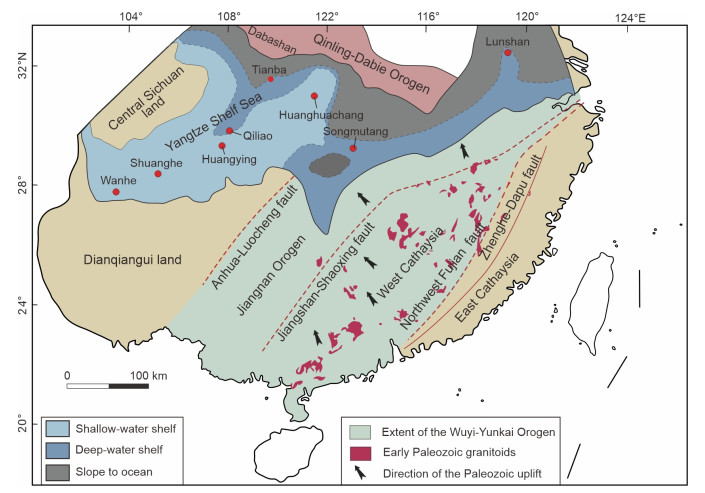
The Ordovician-Silurian transition was marked by extensive volcanic activity globally. In South China, intensive volcanism was documented by abundant ash layers in strata, but the origins and tectonic settings of these ashes remain controversial. This study presents the stratigraphic distribution of volcanic ash layers, zircon trace element and Hf isotope data from the Wanhe Section in the southwestern Yangtze Shelf, providing insights into the tectonic setting and the origin of the parent magmas. The results suggest that volcanic ashes in the southwestern Yangtze Shelf primarily originated from arc magmatism in the Wuyi-Yunkai Orogen, with a mixed source from mantle and crust. The findings corroborate the hypothesis that the Late Ordovician–Silurian Wuyi-Yunkai Orogen in South China represents a collisional orogenic belt.
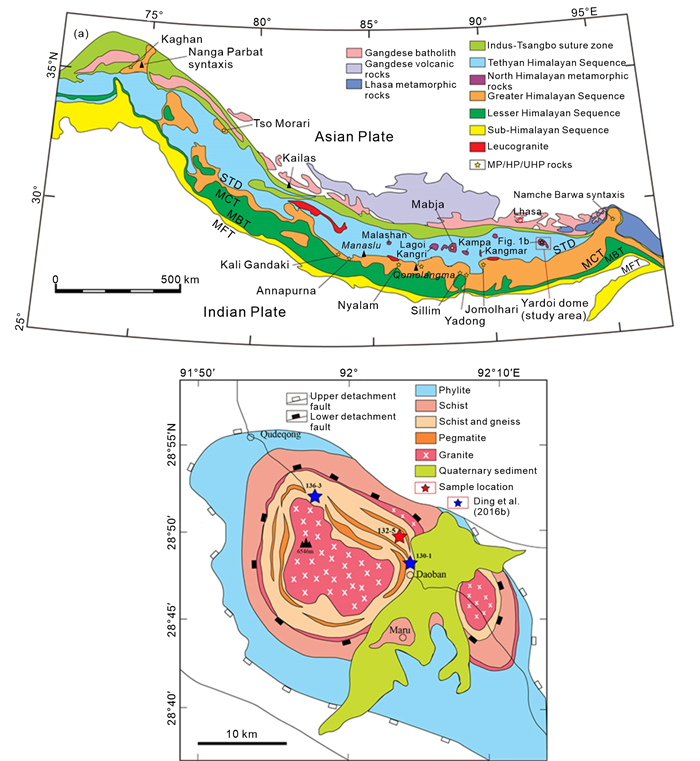
It has long been recognized that garnet has the capacity to preserve the trace element and isotopic signature of distinct metamorphic growth zones because of its high closure temperature. Combined with the large size of certain garnet porphyroblast, this allows investigating variations in metamorphic conditions such as pressure, temperature, deviatoric stress, and fluid composition, which occur during subduction-related metamorphism. Here, one garnet porphyroblast of 6 cm diameter was sampled from the Yardoi schists of Tibet, and the major-, trace-, and Li-Mg isotopic compositions of distinct growth zones were determined
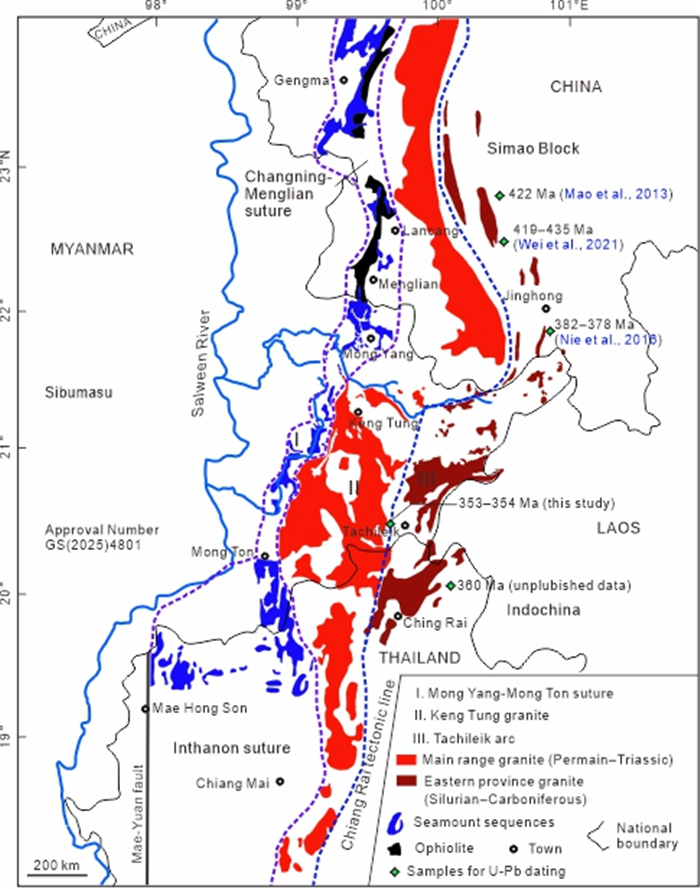
Eastern Myanmar is the key position linking between SW Yunnan and northern Thailand for better understanding of Tethyan evolution. However, the actual location and evolution of the Tethyan suture zone are still unclear in eastern Myanmar. The present study focuses on the geochronological, geochemical and zircon Lu-Hf isotopic study on the plutonic rocks, including granite, diorite and gabbroic rocks, from the Tachileik area, eastern Myanmar. These plutonic rocks yielded zircon U-Pb weighted mean ages of ca. 353–355 Ma, suggesting the Early Carboniferous emplacement. The Tachileik granites are high-K calc-alkaline, weakly peraluminous and have low P2O5 contents, which are typical features of Ⅰ-type granites. They have positive zircon
Zircon U-Pb ages, major and trace elements and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope data of the diabase in the Zhangjiakou District were studied to investigate its derivation and tectonic implications. Zircon U-Pb ages indicate that the diabase was emplaced at ~130 Ma or younger, and captured zircons cluster at ~147, ~240, ~430 and ~465 Ma. The diabase is characterized by minor variations in SiO2 (49.35 wt.%–52.10 wt.%), TiO2 (1.65 wt.%–1.77 wt.%), Al2O3 (17.00 wt.%–18.26 wt.%), MgO (4.28 wt.%–4.93 wt.%), CaO (6.69 wt.%–7.90 wt.%) and Mg# (48–54). It has no significant Eu anomaly and displays enrichment in large ion lithophile elements (Rb, Ba and Sr) and depletion in high field strength elements (Nb, Ta, P and Ti). The diabase exhibits homogeneous Sr ((87Sr/86Sr)i = 0.706 06–0.707 01) and Nd (
The Chinese Altai, a key component of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB), represents a significant Phanerozoic accretionary orogenic belt. The oceanic-continental subduction processes spanning the Cambrian to Carboniferous and subsequent intracontinental extension since the Triassic have been well documented in the Chinese Altai, the southwestern segment of the CAOB. Deciphering the petrogenetic evolution of this region during the Permian is thus crucial for advancing our understanding of its tectonic transitions. However, the Permian tectonic setting of the Chinese Altai remains contentious. To address this knowledge gap, this study presents new geochronological and geochemical data for the Jiangjunshan pluton in the southern Chinese Altai. Zircon U-Pb geochronology reveals that the gabbro and two-mica alkali feldspar granite—which collectively constitute the primary lithology of the Jiangjunshan pluton—were emplaced at ~272 ± 3.5 and ~272 ± 1.6 Ma, respectively. Geochemically, the gabbro exhibits pronounced light rare-earth element (LREE) depletion, low Nb/Yb (0.39–0.46) and Ti/V (23.7–25.3) ratios, and trace-element signatures akin to normal mid-ocean ridge basalts (N-MORB). However, its conspicuous Nb-Ta depletion parallels that of island arc basalts. Depleted Hf-Nd isotopic compositions (
Um Solimate emerald deposit is a unique example for the well-known beryl-related schist type. Where, the Be-mineralization is restricted to NNE-trending quartz veins/lenses and as disseminated emerald grains within the altered-metasomatic zones of phlogopite- and graphite-schists. The study of fluid inclusions for the mineralized quartz vein revealed three major groups: (ⅰ) aqueous (H2O-NaCl), (ⅱ) aqueous-carbonic (H2O-CO2-[CH4]-NaCl), and (ⅲ) aqueous-hydrocarbonic (H2O-CH4) FIs. They have been further classified into five types (namely: types 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5) according to number of phases at the room temperature (20 ℃) as well as microthermometric measurements. Based upon the study of fluid inclusions, the initial-ore forming fluid was supposed to be of magmatic nature, characterized by a relatively high temperature of homogenization (
The giant Pulang porphyry copper deposit, located in the southern Yidun arc segment of southeastern Tibetan Plateau, represents one of the region's largest mineral systems. This study employs numerical simulation to unravel its metallogenic processes. By integrating field-based geological observations with mineralogical and geochemical data, we developed a coupled model encompassing five key stages of ore formation. The simulation successfully reproduced thermal anomalies and accurately predicted the spatial distribution of mineralization zones at Pulang. Coupling dynamic modeling results with chalcopyrite precipitation rates and average Cu grades enabled quantitative estimation of deposit formation duration (0.99–1.22 Ma). Compared with conventional geochronological approaches, this process-constrained modeling framework provides unprecedented insights into the thermodynamic mechanisms controlling porphyry copper system evolution, offering valuable implications for regional exploration strategies.
Understanding the formation of lithium-rich pegmatites is critical for meeting global lithium demand. The 509 Daobanxi Li pegmatite deposit, located in the West Kunlun orogenic belt of northwestern China, represents a significant example of an LCT-type (Li-Cs-Ta) pegmatite system. This study investigates the paragenetic sequence of lithium (Li) minerals and the factors controlling their crystallization, providing new insights into the magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of rare-element pegmatites. Pegmatite dikes exhibit distinct zonation, comprising a wall rock zone, a border zone (aplitic layer), and a core zone (pegmatitic layer), with Li mineralization concentrated in the pegmatitic and aplitic layers. The primary Li minerals include spodumene (Spd), montebrasite (Mbs), eucryptite (Ecr), elbaite (Elb), and lepidolite (Lpd), which crystallize in the order of spodumene → montebrasite → elbaite → lepidolite. Spodumene, the dominant Li-bearing mineral, crystallizes from a Li-saturated melt during the magmatic stage. Montebrasite, a Li-phosphate mineral, forms in P-rich environments, coexisting with spodumene and columbite-group minerals (CGM). During the magmatic-hydrothermal transition, elbaite crystallizes from a B-rich melt, exhibiting skeletal and patchy zoning due to undercooling and disequilibrium crystallization. Hydrothermal alteration leads to the breakdown of spodumene and the formation of secondary minerals such as eucryptite and lepidolite, with lepidolite being the final Li-bearing phase, enriched in fluorine. The coupled dissolution-precipitation processes during the magmatic-hydrothermal transition play a critical role in the remobilization and enrichment of rare elements such as Li, Nb, Ta, and Sn. This deposit, characterized by spodumene crystallization in the Spd + Quartz stability field (≥300 MPa, ≤725 ℃) and subsequent alteration to Ecr + quartz assemblages (270 ℃, 160 MPa), exhibits broader temperature-pressure conditions exceeding typical global pegmatites like Tanco, with no petalite formation observed due to its persistent exclusion from petalite stability fields throughout mineralization. The shear zone controls the pegmatite emplacement and lithium enrichment in the 509 Daobanxi lithium deposit, and its deformation-fluid coupling mechanism provides new insights for the exploration of LCT pegmatite deposits. The present study highlights the importance of understanding both magmatic and hydrothermal processes in the formation of LCT-type pegmatites and provides valuable insights for the exploration of critical metal resources in similar geological settings.
Water-soluble organic acid anions (WSOAA) in subsurface water have been intensively studied during past several decades. They are used as natural gas precursor, tracer for the movement of underground fluid, indicator for porosity improvement, and detecter of deep subsurface life on the Earth. However, little is known about the distributions and origins of organic acids at deep-ultradeep depth underground. Herein, we collected twenty-nine source rock samples covering a wide maturity range from the Ordos, Qinshui, Junggar, Minhe, and Southern North China basins, as well as six subsurface water samples with depth between 6 544 and 8 396 m from industrial gas producing wells in the Tarim Basin, China. We carried out pyrolysis experiments at various temperatures (250–450 ℃) to investigate the role of water on the generation of organic acids. Results show that there are considerable amounts of WSOAA detected in both high-over mature source rocks and deep-ultradeep subsurface water. WSOAA mainly consists of monocarboxylates, predominately formate and acetate. High-TOC oil-generating source rock has low production rate of organic acids due to lack of hydrogen. Different source rocks have distinct ratios of formate to acetate concentration, expressed as
The 128.6-m-thick, shale-dominated Klimoli, Wulalike and Lashizhong formations exposed at the Hatuke Creek Section in the Zhuozishan area of Inner Monglia, North China, have been investigated for conodonts. Detailed stratigraphical collections of conodonts preserved on bedding planes from graptolitic shales, supplemented by additional discrete conodonts acid-leached from limestones, enable a refinement of the conodont biostratigraphic scheme at this section. Four successive conodont biozones, ranging in age from mid Darriwilian to late Sandbian (Stage slices Dw2–Sa2), are identified: the
Carbonates present complex pore systems that strongly influence the physical properties and their interrelationships. This study proposes a new approach to establish pore-type mixing-based permeability transforms by integrating well-log and core data. We investigate the influence of pore-structure heterogeneity on permeability and velocity through the rock-frame flexibility factors (
Fracture-cave reservoirs are widely developed in carbonate formations and account for over 55% of global petroleum reserves. The productivity, formation mechanisms, and
The Changxing Formation of the Upper Permian in the Sichuan Basin remains a focal area for natural gas exploration. Previous research on this formation has predominantly focused on platform-margin reefs in northeastern Sichuan Basin, while reservoirs within the platform have received limited attention. This study addresses this gap by systematically analyzing bioclastic shoal reservoirs in the Zhongjiang-Moxi region of central Sichuan Basin, using integrated methods including core observations, petrographic analysis, well log interpretation, and 3D seismic data. Results reveal that the study area primarily hosts porous bioclastic limestone reservoirs, characterized by storage spaces dominated by intragranular and interparticle dissolution pores. These reservoirs exhibit distinct facies-controlled attributes. Key controlling factors include: (1) syn- to penecontemporaneous karstification, (2) sea-level fluctuations governing reservoir thickness and stacking patterns, (3) micro-paleogeomorphic variations influencing early exposure dissolution, and (4) dolomitization enhancing reservoir quality. Based on these findings, two depositional evolution models for intraplatform reservoirs of the Changxing Formation are proposed.
Co-seismic landslides are a critical secondary hazard of earthquakes in mountainous regions and are driven by a combination of seismic, geological, and geomorphic properties of both the earthquake source and the affected hill slopes. On Sept. 5, 2022, an
The reservoir landslide is typically characterized by high-speed movement of a particle-fluid mixture, and its flow and deposit mechanisms are complex. This paper presents the mechanism of submerged granular column collapse under different densities ambient fluids based on coupled computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD-DEM) analysis. Important fluid-particle interaction forces, such as the drag force and the buoyancy, are considered by exchanging interaction forces between the CFD and DEM computations. We focus on the flow and deposit characteristics of submerged granular column collapse, namely the runout distance, the tail end height, the particle velocity, the energy, and deposit morphology, which are analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively. The change in fluid field caused by submerged granular column collapse and the formation of eddies are also discussed. A relatively dense fluid can significantly hinder the motion of granular flow, but can improve the conversion efficiency of kinetic energy from the vertical to the horizontal direction. Moreover, the eddies caused by fluid turbulence erode the surface of the granular pile, which is especially marked in a high-density fluid. The findings can provide vital theoretical support for the flow and deposit characteristics of granular flow under fluid and offer insights for the study of reservoir landslides.
Altered rock, often encountered in major engineering projects, can seriously affect the stability of rocks and slopes surrounding deeply buried tunnels. This study addressed the alteration mechanism, alteration degree classification, and mechanical parameters of altered rock in engineering project areas using field testing, thin slice identification, X-ray diffraction, and major element testing. Results showed that the altered rock types in the areas of the Pingjiang Pumped Storage Power Station, Hunan Province, and a diversion tunnel in northern Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region include biotite granodiorite, biotite monzogranite, and cataclastic granite, and that the main alteration mechanisms are chloritization of biotite and clayization of feldspar minerals. The altered rocks were classified as slightly, moderately, or strongly altered according to their apparent characteristics, rebound value, longitudinal wave velocity, metamorphic mineral content, and porosity. The bulk density, elastic modulus, cohesion, and internal friction angle (Poisson's ratio) of the altered rocks decreased (increased) with increase in the degree of alteration. Numerical simulations showed that in altered rock slope areas, the zone of strong rock alteration and the moderate-strong alteration contact zone exhibit locally large deformations that represent a certain hazard to engineering projects. These results provide valuable guidance and support for major projects in altered rock areas.
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) represents the largest pool of reactive carbon on the Earth and plays a crucial role in various biogeochemical processes and ecosystem functions. However, it is understudied for a global understanding of DOM molecular properties such as molecular weight, stoichiometry, and oxidation state, and the linkages among them across Earth systems. Here, a meta-analysis of 2 707 sites in 204 literatures was conducted by synthesizing four representative molecular properties of DOM, i.e., mass, double bond equivalent (DBE), modified aromaticity index (AImod), and nominal oxidation state of carbon (NOSC). By exploring H/C and O/C ratios, we examined the relationships among these DOM properties across waters and land systems, and their geographical patterns and environmental drivers. We found that, compared to land system, the mass, DBE, and AImod were all significantly higher in water systems, with river sediments exhibiting the highest values. The DOM oxidation state indicated by NOSC was greater on average in wastewater (NOSC = 0.226 ± 0.06) and marine water (NOSC = 0.133 ± 0.06) than in other habitats. Compared to waters, the mass in land system showed more strongly positive correlations with oxidation states such as NOSC and O/C, and the NOSC showed stronger relations to bioavailability properties such as DBE, AImod, and H/C. Among all the properties, H/C and AImod contributed to the most variations in global DOM properties. In waters, NOSC monotonically increased towards high latitudes, while DBE and AImod showed significant hump-shaped patterns indicating peaked unsaturation and aromaticity at mid-latitudes of approximately absolute 30°–50°. The variations in DOM properties were significantly correlated with environmental factors such as annual mean temperature and pH. Collectively, we revealed the spatial distribution and environmental drivers of DOM molecular properties across Earth ecosystems, which could shed light on our comprehensive understanding of DOM characteristics and its dynamics.
Estimation and attribution of evapotranspiration (
The groundwater (GW) in the floodplain riparian area frequently interacts intensely with surface water (SW). Heat as a tracer is one of the hot research fields in investigating GW-SW interactions, and analytical approaches have been proposed for the calculation of exchange flow velocity. However, few studies have considered the effects of very dynamic flow conditions and monitoring instrumentation on the calculation with field measured data. Herein, taking the middle reaches of the Heihe River as the study area, different types of monitoring wells were constructed under the riverbed and near the river, and multiple methods (Darcy's law, heat tracing, and isotopic mixing methods) were employed to trace the exchanges between the river and groundwater. The results indicate that different methods demonstrate diverse information with obvious unevenly distributed flux along the vertical direction. And the combination of multiple methods has an important role in studying the interaction between GW and SW. Fully screened wells produce intraborehole flow and disturb the heat transport, which is relevant to flow velocity, and further affects the temperature distribution, impacting the temperature-based flow velocity calculation. Dynamic flow conditions aggravate riverbed sediment disturbances, e.g., scour and deposition, and additionally affect the interaction and monitoring data.
Ice cores play an important role in the reconstruction of historical atmospheric information. The glacier of the Tibetan Plateau is influenced by the Indian monsoon and westerly winds, which divide the Tibetan Plateau into monsoon- and westly influenced regions. These atmospheric circulations bring distinct microbial communities to glaciers, with the microbial dispersal process being also influenced by atmospheric factors. However, the potential influence of between bacterial abundance and atmospheric factors is not well known. To reveal potential mechanisms controlling bacterial abundance between two regions, we obtained bacterial abundance and atmospheric records for the past 46 years from two ice cores located within these regions. Statistical regression models were constructed to fit the relationship between bacterial abundance and atmospheric factors. Generalized additive model (GAM) was superior in modeling bacterial abundance compared with linear models and showed that the key factors affecting bacterial abundance were different in the monsoon- and westerly-dominated regions. Specifically, atmospheric dust and black carbon were the key factors for the monsoon-dominated region, and westerly index was the key factor for the westerly-dominated region. The model outputs confirm that atmospheric black carbon plays an important role in affecting bacterial abundance for the glacier located within the monsoon-dominated region, particularly in recent decades. The model also predicted that bacterial abundance will increase by 27% with a doubled black carbon deposition. We quantify and model for the first time that relationship between bacterial abundance and atmospheric black carbon in Tibetan glaciers change over time based on GAM models.
The sediments of crater lakes are one of the ideal archives for high-resolution paleoenvironmental reconstruction. This paper presents sedimentary records of 21 crater lakes in monsoonal China and systematically discusses the geographical distribution and formation ages of these crater lakes. Sediment provenance of the crater lakes and its influencing factors were analyzed, and paleoenvironmental sequences and human activities records on different timescales reconstructed by crater lake sediments in monsoonal China were reviewed. The following points are highlighted: (1) Crater lakes in monsoonal China have been shown to preserve continuous long-time sediments that can exceed even 400 ka, although the chronology of some sediments in the southern part is debated and there were currently fewer long time records from the northern part; (2) the sediment provenance of crater lakes in northern China (e.g., aeolian inputs) was different from that in the south (e.g., the volcanic-lake rim), due to the different location and deposition conditions of crater lakes; (3) crater lake sediments have been used to reconstruct the history of climate changes on different timescales, but reconstruction studies of glacial-interglacial and decadal-annual scale records and studies of spatial comparisons of records on different timescales still need to be strengthened; (4) the anthropogenic signals, which include cultivation, logging, and industrial activity, are well documented in crater lake sediments from different areas and can therefore provide key evidence for the study of the Anthropocene.
A comprehensive understanding of the hydrological cycle is essential for Earth system science and climate change research. The Water Cycle Intensity (WCI) is defined as the sum of precipitation and actual evapotranspiration within a landscape unit. It is a widely used metric to quantify the impact of climate change on the global distribution of water resources. The WCI in the Pamir Plateau, located at the heart of Asian Water Towers, has received little attention. Understanding this aspect is crucial for assessing the impact of climate change on the hydrological cycle and devising strategies to adapt to these changes. Our study assessed the spatiotemporal variation in WCI on the Pamir Plateau from 1980 to 2019 using the WCI framework. Additionally, we explored the teleconnection mechanisms linking the WCI with the Indian Ocean Dipole Mode Index (DMI), canonical El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), and El Niño Modoki (EMI) using the wavelet analysis method. The findings showed that the WCI of the Pamir Plateau experienced a statistically insignificant increase from 1980 to 2019, particularly after 2003. Spatially, the eastern Pamir Plateau WCI increased significantly, whereas the western region showed a non-significant downward trend. This study found that the WCI in the Pamir Plateau is significantly influenced by atmospheric circulation patterns, and the variation in the WCI in the Pamir Plateau is mainly affected by the canonical ENSO, as well as by the coupling effect of canonical ENSO, and EMI. In addition, based on the characteristics of the regional hydrological cycle, we developed water resource management policies targeting flood risks in the northern Pamir Plateau and drought trends in the southwestern region. These insights not only deepen our understanding of changes in terrestrial hydrological cycles and their underlying mechanisms under climate change but also provide important references for water resource management in the mountainous regions of Central Asia.
The Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen holds numerous glaciers crucial for the Asian Water Tower, thus influencing the surface energy balance and climate feedback. Understanding glacier fluctuations is essential for improving our knowledge of current and future glacial evolution, but limited by short modern glacial observations. Proglacial lakes provide valuable opportunities to obtain high-resolution and continuous glacial changes, but detailed investigations remain scarce. For example, there is still controversy over whether lake sediments reflect melting or ablation. Therefore, we selected a modern glacial lake in the Himalayan region, formed due to glacial retreat in the 1960s, and compared its sedimentary records with modern observations. This provides a case study for future reconstruction of glacial changes using lake sediments. Our results indicate that the sediments of the proglacial lake are primarily influenced by glacial meltwater. Stronger meltwater fluxes transport more debris, magnetic minerals, and terrestrially derived organic matter to the lake. In terms of grain size distribution, the fine silt component (2–8 μm) can serve as an indicator of glacial meltwater intensity. Additionally, this study reveals an opposite trend between glacial meltwater variations and air temperature trends over the past few decades. This suggests that evaporation may offset the increase in glacial meltwater, though the multi-century (> 100-year) trend requires validation with longer records.
Compound extreme climate events may profoundly affect human activity in the Yangtze River Basin. This study analyzed the long-term spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of compound heatwave-drought and heatwave-waterlogging events in the Yangtze River Basin using multi-period historical observation data and future scenario climate model data. It also examined the changes in population exposure to compound extreme climate events in the basin and their driving factors by combining population statistics and forecast data. The results show that the occurrence days of compound heatwave-drought and heatwave-waterlogging events in the Yangtze River Basin have shown a significant upward trend both in historical periods and future scenarios, accompanied by a marked expansion in the affected areas. Compared to historical periods, population exposure in the Yangtze River Basin under future scenarios is expected to increase by 1.5–2 times, primarily concentrated in the key urban areas of the basin. The main factors driving the changes in population exposure are the increased frequency of extreme climate events and population decline in future scenarios. These findings provide scientific evidence for early mitigation of meteorological disasters in the Yangtze River Basin.
The crystallinity has the potential to distinguish the primary and secondary calcite in Chinese loess, which then provides insights into illuviation depth and variations of the East Asian Summer Monsoon. However, this aspect has been rarely investigated. In this study, we defined the crystallinity of calcite as the height/area (
ISSN 1674-487X
CN 42-1788/P
Editor in Chief: Yanxin Wang
Executive Editors in Chief: Zhong-Qiang Chen, Jiang Shaoyong
Associate Editor:
Shu Jiang,Changdong Li,Rui Ma
Qiliang Sun,Timothy M. Kusky,Dun Wang
Lunche Wang,Long Xiao,Xin-Fu Zhao
Keqing Zong,Renguang Zuo ,Zongjun Yin
2024 Impact Factor 4.7, JCR Q1
JES Citing RankingMore +
- 1Seawater Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen over the Past 500 Million Years
- 2Inventory and Spatial Distribution of Landslides Triggered by the 8th August 2017 MW 6.5 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake, China
- 3Geological Evidence for the Operation of Plate Tectonics throughout the Archean: Records from Archean Paleo-Plate Boundaries
- 4Proto-South China Sea Plate Tectonics Using Subducted Slab Constraints from Tomography
- 5An Optimized Random Forest Model and Its Generalization Ability in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping:Application in Two Areas of Three Gorges Reservoir, China
- 1Dynamic hydromechanical behavior of reservoir slopes: Seepage and deformation under variable water level drawdown
- 2Automatic Stitching Method for Chang'E-2 CCD Images of the Moon
- 3Radial anisotropy in the crust beneath the northeastern Tibetan Plateau from ambient noise tomography
- 4Spatial Variation of Hydraulic Conductivity Categories in a Highly Heterogeneous Aquifer: A Case Study in the North China Plain (NCP)
- 5On the Numerical Modeling of the Deep Mantle Water Cycle in Global-Scale Mantle Dynamics: The Effects of the Water Solubility Limit of Lower Mantle Minerals
- 1Sedimentary Characteristics and Reservoir Prediction of Paleogene in the East Part of Kuqa Foreland Basin
- 2Chemical Composition of Urban Street Sediments and Its Sources
- 3Hydrocarbon Distribution and Accumulation Model in the South of Lixian Slope, Raoyang Subbasin
- 4Rainfall Threshold Calculation Method for Debris Flow Pre-Warning in Data-Poor Areas
- 5Deepwater Canyons Reworked by Bottom Currents: Sedimentary Evolution and Genetic Model
Recommended IssuesMore +
- Satellite remote sensing monitoring and its applications in major engineering projects
- Continental Margins of East and Southeast Asia: Sedimentology, Geomorphology, and Climate change Special Issue in The Journal of Earth Science
- Notice on Collecting “Top 70 Questions Facing Earth Science”
- Call for papers for a special issue of Journal of Earth Science: on Sustainable Technologies for Earth Science and Climate Change
- Tropical Large Benthic Foraminifera: Adaption, Extinction, and Radiation